Hogyan készítsünk a letöltött ISO fájlunkból bootolható pendrive -ot linux alatt?
A válasz viszonylag egyszerű, egy régi és jól bevált programmal, a dd paranccsal természetesen.
A videóban a HaikuOS 64 bites verzióját töltöttem le, mert azzal még igazából sosem volt dolgom, a BeOS időkben meg ugye még nem is létezett ilyesmi, legalábbis az én környezetemben. Gyakorlatilag mindenki Debiant, Win98 -at és WinXP -t használt… 😀
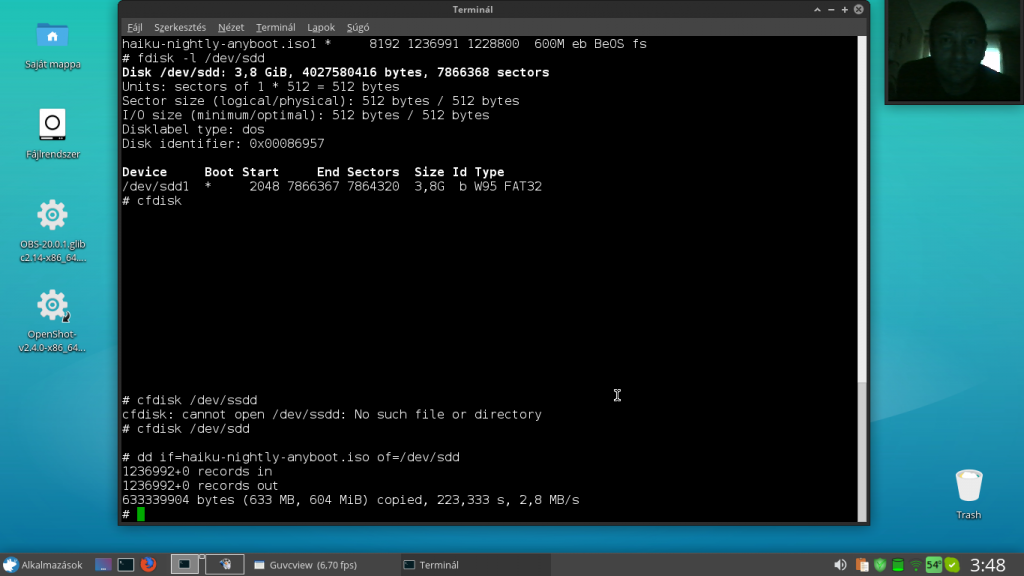
A folyamat végén látható felirat, amit már ugye nem vártam meg:
# dd if=haiku-nightly-anyboot.iso of=/dev/sdd 1236992+0 records in 1236992+0 records out 633339904 bytes (633 MB, 604 MiB) copied, 223,333 s, 2,8 MB/s
A dd parancs kicsit részleteseebben a beépített súgó alapján, jól láthatóan azért elég sok opció érhető el:
# dd --h Usage: dd [OPERAND]... or: dd OPTION Copy a file, converting and formatting according to the operands. bs=BYTES read and write up to BYTES bytes at a time cbs=BYTES convert BYTES bytes at a time conv=CONVS convert the file as per the comma separated symbol list count=N copy only N input blocks ibs=BYTES read up to BYTES bytes at a time (default: 512) if=FILE read from FILE instead of stdin iflag=FLAGS read as per the comma separated symbol list obs=BYTES write BYTES bytes at a time (default: 512) of=FILE write to FILE instead of stdout oflag=FLAGS write as per the comma separated symbol list seek=N skip N obs-sized blocks at start of output skip=N skip N ibs-sized blocks at start of input status=LEVEL The LEVEL of information to print to stderr; 'none' suppresses everything but error messages, 'noxfer' suppresses the final transfer statistics, 'progress' shows periodic transfer statistics N and BYTES may be followed by the following multiplicative suffixes: c =1, w =2, b =512, kB =1000, K =1024, MB =1000*1000, M =1024*1024, xM =M GB =1000*1000*1000, G =1024*1024*1024, and so on for T, P, E, Z, Y. Each CONV symbol may be: ascii from EBCDIC to ASCII ebcdic from ASCII to EBCDIC ibm from ASCII to alternate EBCDIC block pad newline-terminated records with spaces to cbs-size unblock replace trailing spaces in cbs-size records with newline lcase change upper case to lower case ucase change lower case to upper case sparse try to seek rather than write the output for NUL input blocks swab swap every pair of input bytes sync pad every input block with NULs to ibs-size; when used with block or unblock, pad with spaces rather than NULs excl fail if the output file already exists nocreat do not create the output file notrunc do not truncate the output file noerror continue after read errors fdatasync physically write output file data before finishing fsync likewise, but also write metadata Each FLAG symbol may be: append append mode (makes sense only for output; conv=notrunc suggested) direct use direct I/O for data directory fail unless a directory dsync use synchronized I/O for data sync likewise, but also for metadata fullblock accumulate full blocks of input (iflag only) nonblock use non-blocking I/O noatime do not update access time nocache Request to drop cache. See also oflag=sync noctty do not assign controlling terminal from file nofollow do not follow symlinks count_bytes treat 'count=N' as a byte count (iflag only) skip_bytes treat 'skip=N' as a byte count (iflag only) seek_bytes treat 'seek=N' as a byte count (oflag only) Sending a USR1 signal to a running 'dd' process makes it print I/O statistics to standard error and then resume copying. Options are: --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> Report dd translation bugs to <http://translationproject.org/team/> Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/dd> or available locally via: info '(coreutils) dd invocation'